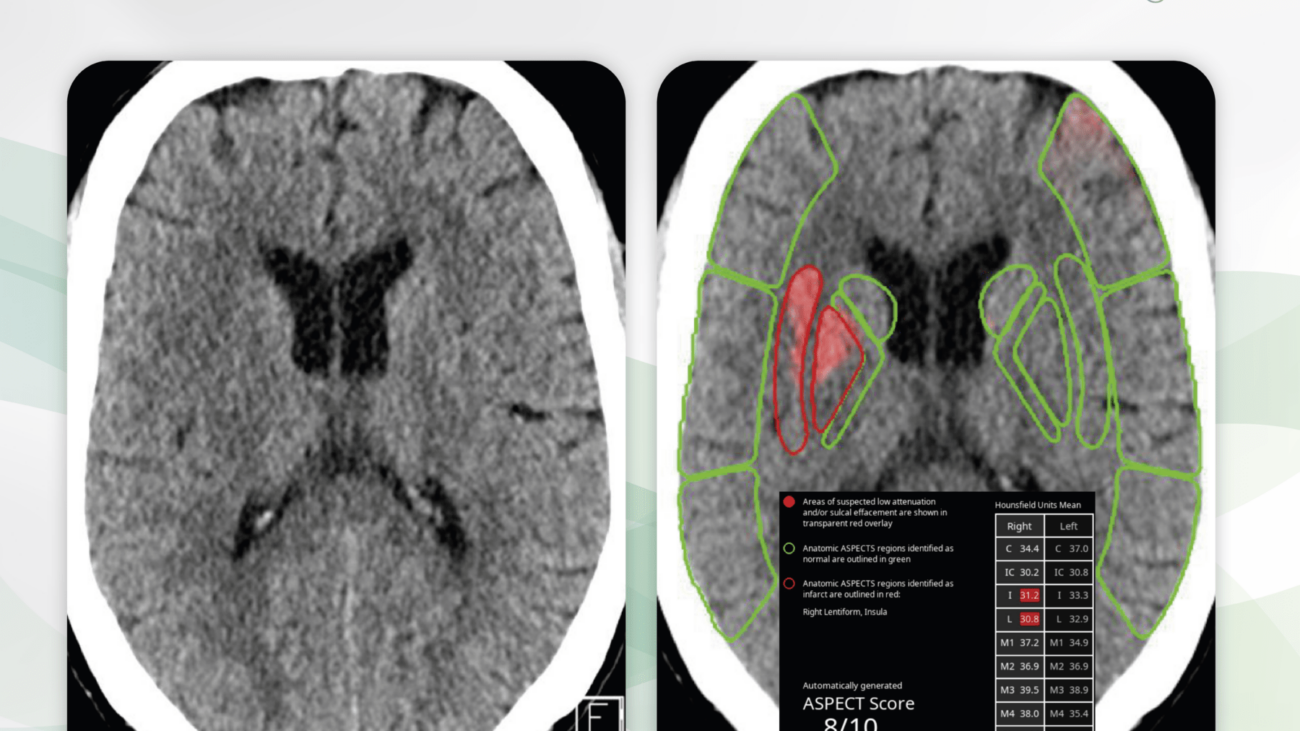
Non-enhanced cerebral CT of a 47-year-old patient with acute left sided paresthesia about 4 hours before the examination. Slightly low attenuation of the right lentiform nucleus and the right insular cortex is particularly visible when comparing the sides. No intracranial hemorrhage is visible (links). CINA-ASPECTS identifies the hypodensities and correctly assigns them to the lenticulostriatal territory (right, red). In addition, the results are tabulated, the ASPECTS is calculated as 8/10.
Time is Health: Our motto is particularly understandable when it comes to acute ischemic strokes. Every medical acute care unit knows what it means to accompany a large number of patients around the clock with the best diagnostic precision. Intracranial acute pathologies must be visualized quickly and safely.
It is with great pleasure that we present CINA-ASPECTS, an AI assistant for the detection of acute intracranial ischemia in CT studies.
Why CINA-ASPECTS matters abd how it works
CINA-ASPECTS was developed as a triage tool for emergency radiology. The AI assistant immediately reports suspected acute intracranial ischemia in CT studies and enables the prioritization of these patients. The AI assistant provides radiologists and emergency physicians with an outstanding presentation of the findings in words and images.
Any medical professional can use CINE-ASPECTS for each individual emergency patient by quickly and easily uploading cerebral CT studies to Radailogy. In medical institutions, this AI assistant can also do its work automatically in the background in order to fully exploit the desired triage potential.
Who benefits
The triage of acute ischemic strokes is essential for everyone involved, i.e., patients, clinicians and radiologists.
Our own experience at Radailogy
We were able to reproduce the statistical data of sensitivity of 76.6%, specificity of 88.7% and of accuracy of 87.0% given by the developer in our tests and partly worked out higher data for accuracy.
CINA-ASPECTS detects low attenuation of the supratentorial tissue and sulcal corticomedullar disorders. The eponymous topographical ASPECTS is used for the analysis: the supratentorial tissue is divided into ten regions of the middle cerebral artery supply per hemisphere to describe ischemia in one of the two hemispheres. The suspected pathological areas are marked in color and listed in a table with information on the mean density values per region. From this, the ASPECTS for both hemispheres is calculated and given.
The developer cites as a limitation that older infarctions would not be correctly identified and describes the use of CINA-ASPECTS within 100 minutes of the clinical event as an essential inclusion criteria.
CINA-ASPECTS does not currently support the detection of posterior circulation ischemia (pc-ASPECTS). We expect this with the next upgrade.
We also evaluated CINA-ASPECTS together with two other AI assistants, CINA-ICH and CINA-LVO, which were developed to detect hemorrhagic and non-hemorrhagic strokes in CT studies. Find out more in our AI assistants!
The scientific evidence
Ayobi A, Chang P, Chow D, Filippi C, Quenet S, Tassy M, Chaibi Y. Validation of a Deep Learning AI-based Software for Automated ASPECTS Assessment. ECR 2023. DOI: 10.26044/ecr2023/C-19206
Data to upload to Radailogy
Non-enhanced cerebral CT studies of any CT scanner; axial reformations; minimal matrix size 256 x 256; maximal slice thickness 2.5 mm; tube current 100 kVp to 160 kVp (recommended 120 kVp to 140 kVp); soft tissue reconstruction kernel