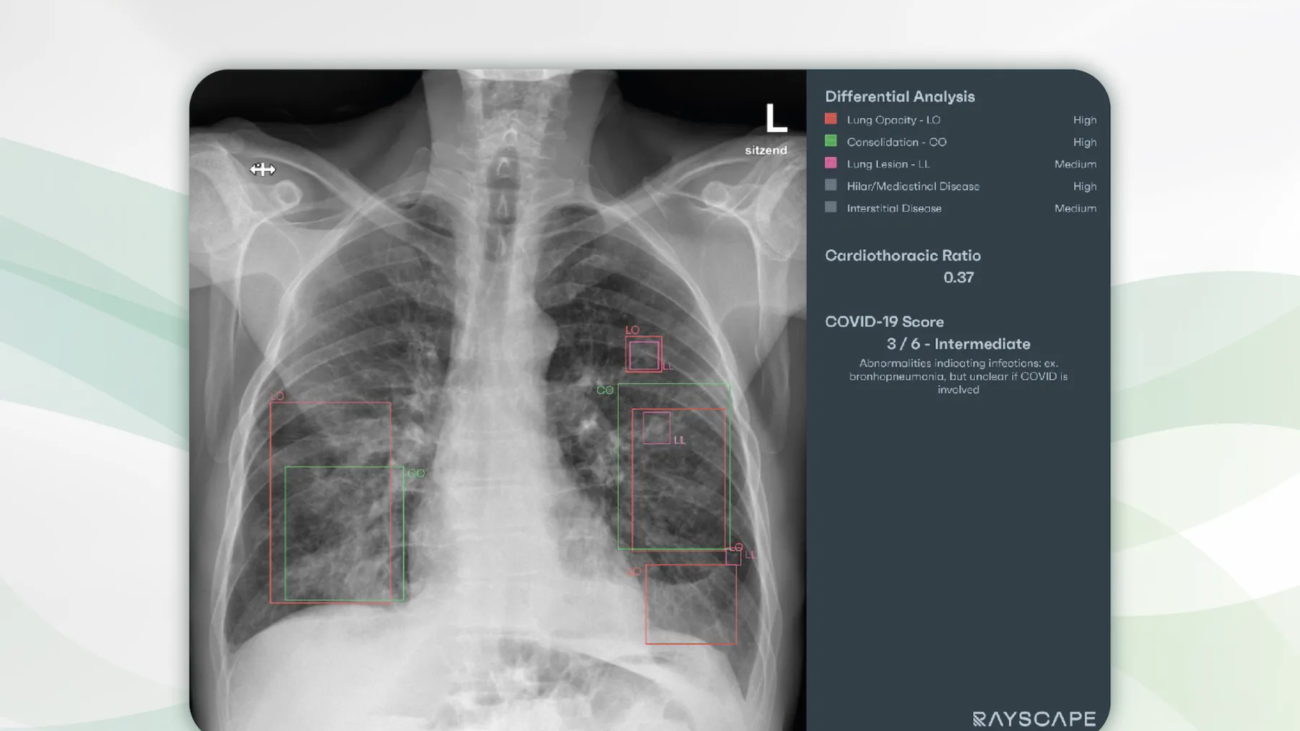
Chest radiography of a 65 years old patient with symptoms of lower respiratory tract infection. Multiple lung opacities and consolidations are visible in projection to the lower lung lobes as well as the middle lobe. Rayscape correctly identifies all consolidations (red) and opacities (green). Rayscape rates the probability for viral disease as intermediate (3 out of 6) and correctly suggests bronchopneumonia as the differential diagnosis. In addition, some small lung lesions are reported (pink) that were initially missed by the radiologists.
Chest radiography is one of the most common radiological examinations of all, and it is also an essential first-line imaging modality in hospitals and doctors´ offices. The precision in reporting and the communication of results from radiologists to patients and clinicians are the most important success factors for any optimal discussion of findings and therapy.
It is with great pleasure that we present Rayscape, an AI assistant for chest radiography.
What Rayscape is and how it works
Rayscape increases accuracy in detecting 17 major thoracic pathologies.
Thoracic findings are reported and visualized in tabular form. For each finding, the true positive rate is presented as a degree of probability versus differential diagnoses, especially for pulmonary nodules, pneumonia, and mediastinal pathologies. The clear presentation of findings is a welcome support for knowledge transfer from radiologists to patients and doctors.
Who benefits
Patients, clinicians and radiologists by identifying the most important chest diseases and injuries with a clear presentation of the findings in words and pictures.
Our own experience at Radailogy
We tested Rayscape for several years and brought it to life with the manufacturer. We reviewed the performance data and compared it to our own observations:
Rayscape supports the detection of pulmonary nodules, pulmonary consolidation, pulmonary edema, pulmonary emphysema, interstitial lung disease, tuberculosis, pneumothorax, pleural effusion, atelectasis, cardiomegaly, hilar and mediastinal pathologies, diaphragmatic abnormalities, fractures, scoliosis, catheters and drains. From our point of view, Rayscape achieves the best results in the detection of pneumonia, including viral pneumonia with probability grading from 1 to 6, pulmonary nodules, pneumothorax, pleural effusions, cardiac decompensation, consolidations and atelectasis.
The performance
Rayscape has a high level of accuracy in detecting 17 major chest pathologies. Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristics (AUROC) is highest for tuberculosis (99.1), pneumothorax (97.4), pulmonary edema (94.7), consolidations (94.6), lowest for interstitial lung disease (81, 5), scoliosis (82), diaphragmatic anomalies (85.4), and hilar and mediastinal pathologies (87.7).
Data to upload to Radailogy
Digital radiography of the chest p.a. or a.p.