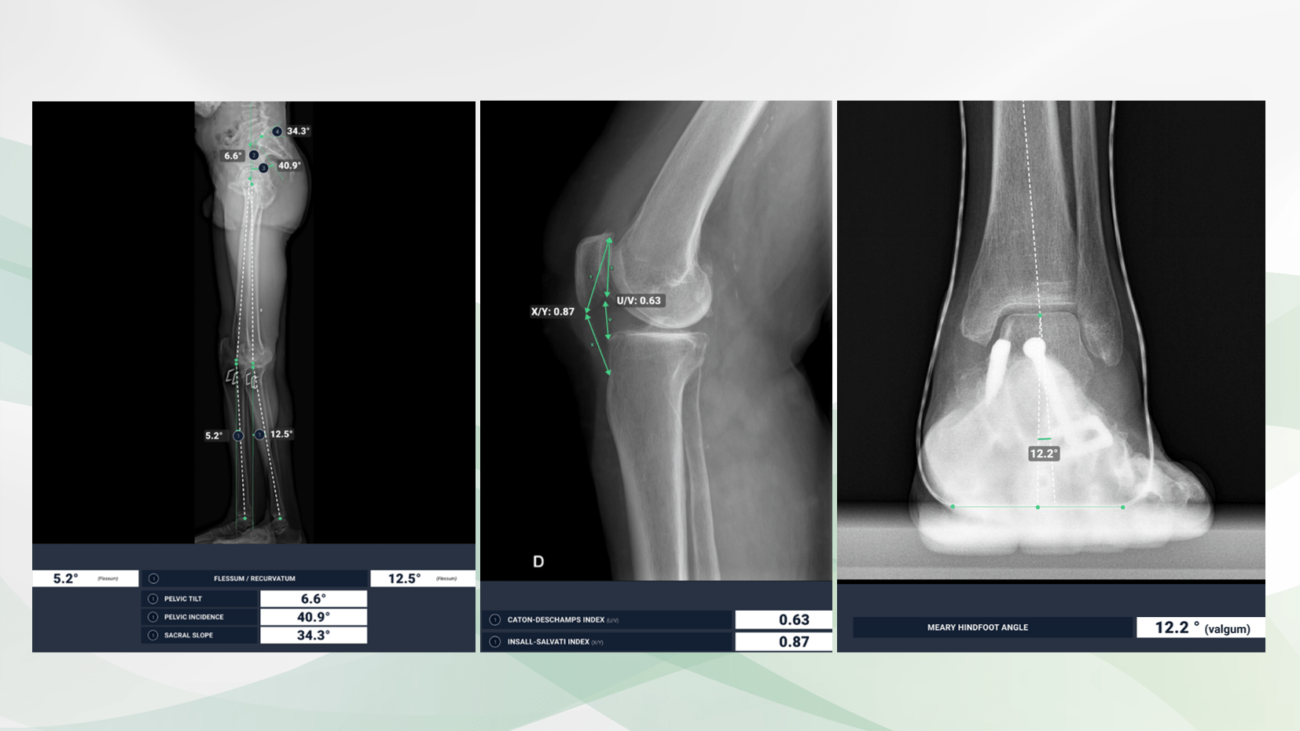
Lateral radiographs of both legs (left) and the right knee joint (middle), radiography of the left ankle and forefoot a.p. (right). BoneView Measurements calculates the iliosacral body axes, the pelvic tilt and the femorotibial joint angles to determine the genu flexum and recurvatum (left). The Caton-Deschamps and Insall-Salvati indices (middle) as well as the Méary hindfoot angle (right) are precisely indicated.
We have the latest upgrade available for you! Gleamer´s BoneView Measurements of body axes come with interesting, new functions.
What is new?
Caton-Deschamps and Insall-Salvati indices
The Caton-Deschamps index is used to measure patellar height and identify patella alta and patella baja. It relies upon the length of the patellar articular surface and its distance from the tibia.
The Insall-Salvati index is the ratio of the patella tendon length to the length of the patella and is used to determine patellar height.
Genu flexum and Genu recurvatum
Genu flexum describes the pathological reduction of full knee extension, also known as flexion contracture. Normal active range of motion is 0° extension and 140° flexion.
In Genu recurvatum, or back knee, the knee bends backwards. In this deformity, excessive extension of the femorotibial joint occurs.
Hindfoot angle on Méary´s views
Méary view X-rays measure the angular deviation of the hindfoot axis in order to assess hindfoot malalignment.
The scientific evidence
van Duijvenbode D, Stavenuiter M, Burger B, van Dijke C, Spermon J, Hoozemans M. The reliability of four widely used patellar height ratios. Int Orthop. 2016 Mar;40(3):493–497.
Kadakia N & Ilahi O. Interobserver Variability of the Insall-Salvati Ratio. Orthopedics. 2003;26(3):321-323.
Neri, R. Barthelemy, Y. Tourné. Radiologic analysis of hindfoot alignment: Comparison of Méary, long axial, and hindfoot alignment views. Revue de Chirurgie Orthopédique et Traumatologique. 2017;103(8):882-887.
Data to upload to Radailogy
Digital radiography of the skeleton