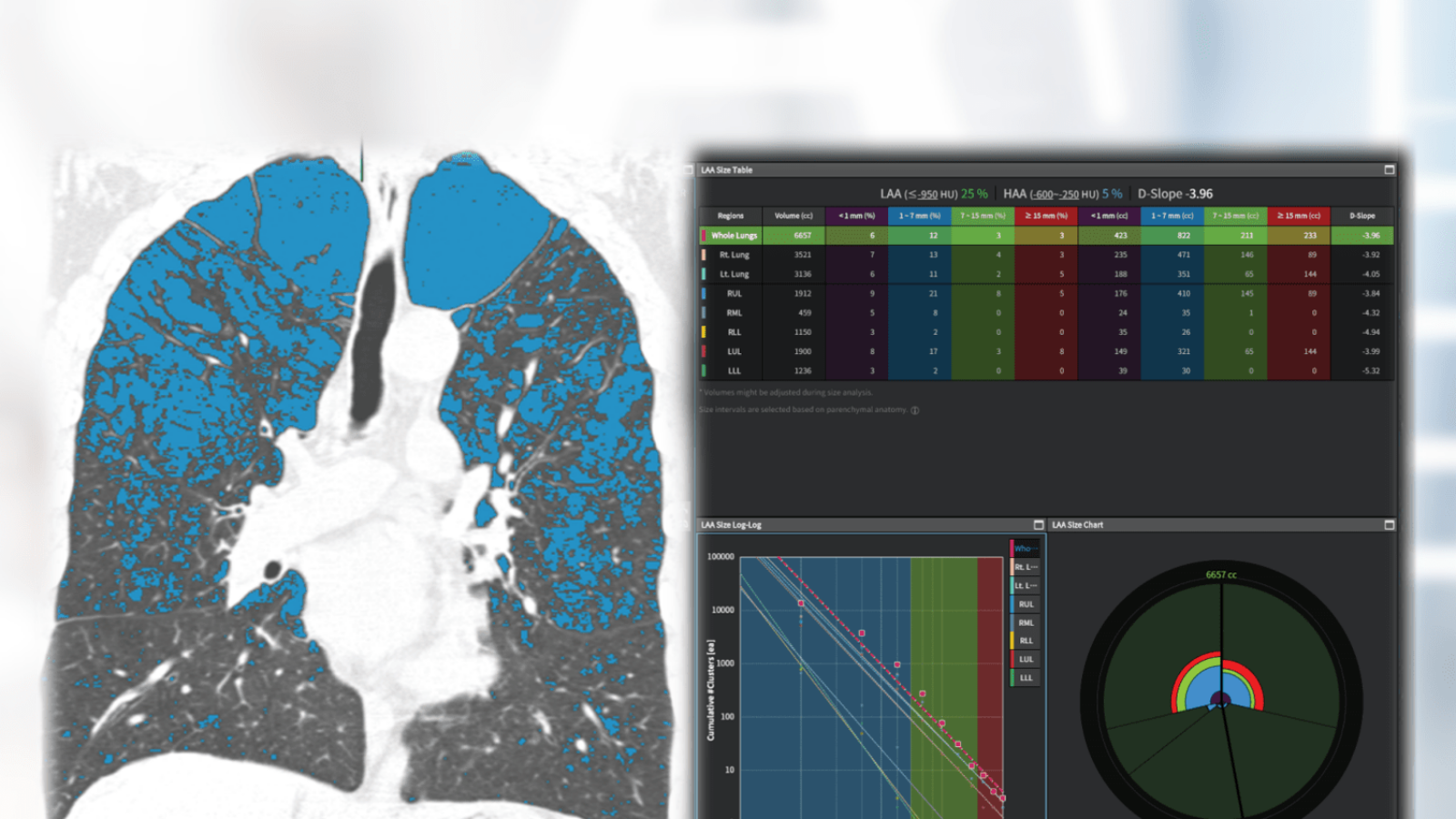
Non-enhanced low-dose chest CT of a patient with COPD. MPR visualization of lung anatomy and emphysema clusters (left) and detailed charts and graphs (right). The absolute volumina and the relative low attenuation volumina (25%) were given for both lungs as well as for each lobe. aview COPD calculated the D-slope as -3.96. This value is considered the diameter of the emphysema clusters plotted against the cumulative number of lesions on a log–log scale. The slope of these linear relationships is calculated, with a steeper slope indicating a smaller emphysema size.
Smokers know that smoking can have serious health consequences. Chronic coughing, mucus buildup, and shortness of breath are already disease symptoms. CT scans are highly predictive of chronic lung damage. But how exactly can this damage be seen? Our new AI assistant helps!
It is with great pleasure that we present aview COPD, an AI assistant for the detection and detailed description of chronic lung diseases in CT studies.
Why aview COPD matters and how it works
The AI assistant classifies and quantitatively analyses two COPD phenotypes, i.e., the airway type and the emphysema type. This automatic segmentation software provides expedite analysis and visualization of the lungs, the lung lobes as well as the pulmonary airways and blood vessels. Functional and pathological lung volumes are precisely calculated. The results are presented through 2D and 3D images, intuitive charts and detailed graphs. An important key feature is the tracking of disease in follow up CT studies. Hence, aview COPD may serve as an imaging biomarker of diagnosis and lung function.
Not only physicians, but also smokers themselves get a clear impression of any pathological lung changes.
Why benefits
In particular, smokers themselves as well as clinicians and radiologists benefit from the detailed presentation and calculation of the lungs with comprehensive data and images.
Our own experience at Radailogy
Coreline reports the AI assistant´s analysis agreement for emphysema, airway and air trapping as 99%, 96% and 99%, respectively. aview COPD offers a variety of MPR images, diagrams and graphs to illustrate the pulmonary anatomy and disease as well as the distribution pattern of COPD. An interesting feature is the analysis and depiction of emphysema clusters using the D-slope value by applying a three-dimensional size-based emphysema clustering technique. For the calculation of D-slope, the diameter of the emphysema cluster is plotted against the cumulative number of lesions on a log–log scale. The slope (D-slope) of these linear relationships is calculated, with a steeper slope (increase in absolute D value) indicating a smaller emphysema size. The airway and lung vessel segmentation, the morphology and pathology of the airway walls and diameter are shown by 3D images and detailed tables. In our opinion, the fissure analysis is of limited help. Overall, the visualized contents enhance the understanding of pulmonary morphology and pathology.
Anyone can use aview COPD by quickly and easily uploading lung CT scans to Radailogy.
We also evaluated aview COPD together with aview LCS and aview ILA, which were developed to detect and quantify pulmonary nodules and evaluate the entire lung structure in CT studies. Find out more in our AI assistant menu!
The scientific evidence
Hwang HJ, Lee SM, Seo JB, Lee JS, Kim N, Lee SW, Oh YM. New Method for Combined Quantitative Assessment of Air-Trapping and Emphysema on Chest Computed Tomography in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Comparison with Parametric Response Mapping. Korean J Radiol. 2021 Oct;22(10):1719-1729.
Hwang HJ, Seo JB, Lee SM, Kim N, Yi J, Lee JS, Lee SW, Oh YM, Lee SD. Visual and Quantitative Assessments of Regional Xenon-Ventilation Using Dual-Energy CT in Asthma-Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Overlap Syndrome: A Comparison with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Korean J Radiol. 2020 Sep;21(9):1104-1113.
Data to upload to Radailogy
Non-enhanced low-dose chest CT studies of any CT scanner; axial reformations; slice thickness and interval 1.0 mm each; lung reconstruction kernel